In the fast-paced world of software development, delivering reliable, high-quality applications requires rigorous testing. But managing large-scale automated testing across multiple teams and application components is a complex challenge - especially in enterprise platforms like Motive Service Management Platform (SMP) To strengthen testing capabilities, the Automated Test Framework (ATF) was integrated into SMP— a powerful, structured testing system designed to simplify the creation, management, and execution of automated tests at scale.
What is the Automated Test Framework (ATF)?
The Automated Test Framework (ATF) is a feature designed to help users automate the testing of applications and configurations on the platform. ATF is much more than a test runner. It’s a unified platform that:
- Enables customers to write and maintain tests close to their application code.
- Allows each application component of SMP to own and manage its own test suites independently, preventing cross-team disruptions.
- Coordinates test execution by leveraging reusable steps and underlying core utilities.
- Produces comprehensive Cucumber reports to track test outcomes and quality metrics.
In essence, ATF orchestrates every piece of your automated testing puzzle — from interpreting test scenarios to managing test lifecycle events and delivering actionable feedback.
The Role of UBDD Core in ATF
At the heart of ATF’s execution capabilities lies the UBDD Core project — a collection of utility methods encapsulating the most common application functionalities:
- UI automation
- REST and SOAP API interactions
- SSH, FTP sessions
- Database operations
These functionalities are the most common ones for all the SMP applications and so the respective implementations should also reside on the core project. This is how UBDD Core project had evolved and now it has implemented each of the above functionalities each with its own utility functions. Users who want to automate their test use cases can add this UBDD core project into their dependencies and start automation.
ATF Quick Start Guide
Get started in minutes:
- The first step is to download the AutomatedTestFramework-<VERSION>.zip (ZIP file). SMP customers can obtain the download link by contacting the SMP maintenance team to get a link to download the SMP release bits.
- Unzip the downloaded package and from the AutomatedTestFramework-<VERSION> directory, run the following command: bin\install.bat (or run bin/install.sh from a Bash shell)
- Edit the src/test/resources/Environment.properties file with Server, port and path pointing to the downloaded Selenium driver
- Run: mvn clean test
- ATF ships with a single example test
(src/test/resources/acme/workflows/interactive/VerifyStartupWorkflow.feature) . This test verifies the basic operation of the StartupWorkflow which is included in the SMP reference configuration. This is akin to the “hello world” example provided with software languages. - Users of the ATF are not limited to step definitions shipped with the ATF. Users can easily create their own feature files to define the specific functionality or workflow they wish to automate — and then execute them seamlessly.
- To create a feature file, follow these steps:
- Open the downloaded ATF project in Eclipse.
- Under src/test/resources, create a new folder. You can organize your folders any way you like for custom steps.
- Right-click the folder, select New File, and name it with a .feature extension—for example, newFunctionality.feature.
- Users can leverage methods in the shipped JAR to implement custom steps, avoiding the need to maintain scripts across SMP releases.
- Method signatures generally remain stable, so most custom steps continue to work, though implementations may need occasional updates.
For example:
Feature file step :
“Then WFL verify the step contains text in header "<expected header text>"
Step definition and method signature:
@Then(" WFL verify the step contains text in header \"([^\"]*)\")
public void verifyWorkflowStepContainsHeader(String header) {
// implementation
}
In the above example, the method signature remains unchanged. Its responsibility is to verify that a workflow step contains the expected header text. Even when the application undergoes enhancements—such as changes to UI structure or data loading behavior, the internal implementation of this method may need to be updated. However, as long as the signature and step definition remain intact, existing feature files continue to work without modification. - This approach is ideal for environments where SMP is customized, allowing minor adjustments without breaking functionality.
- If needed, Motive’s experienced professional services automation experts can assist customers by creating feature files on their behalf, ensuring a smooth and efficient setup process.
Why ATF is a Game-Changer
Modular Ownership of Tests
Each application component owns its tests within ATF. This autonomy allows teams to:
- Manage tests without affecting others.
- Quickly iterate on their features and associated test cases.
- Maintain high test quality with localized responsibility.
Ready-to-Use Test Steps
ATF provides a rich library of predefined steps for common SMP functionalities. No need to build everything from scratch — just plug and play.
Unified Reporting with Cucumber Reports
After test execution, ATF consolidates results into detailed Cucumber reports. These reports:
- Present test outcomes in an easy-to-read, business-friendly format.
- Highlight passed, failed, and skipped scenarios clearly.
- Include step-level details and screenshots (if applicable).
- Help teams quickly identify flaky or failing tests.
- Support data-driven insights for continuous quality improvement.
The use of Cucumber reports bridges the gap between technical test results and stakeholder visibility, making it easier to communicate quality status across the organization.
In the screenshot below, the image on the left shows the overall report for all scenarios across all feature files. When you click on a feature file name, it displays the stepwise report for the selected scenario, as shown in the image on the right.

Extensible by Design
Need something custom? Easily extend the predefined steps to add your own logic without breaking the base functionality.
Maintained by Motive
Don’t worry about changes in the application. SMP team keeps the steps updated, so your tests remain stable even when the UI evolves.
Consistent & Reliable Automation
With centrally maintained steps and best practices built-in, your tests are more robust and consistent across teams.
Promotes Reuse & Reduces Duplication
Write once, use many times. Shared steps avoid repeated code, saving effort and reducing maintenance overhead.
Accelerates Upgrades and Ensures Quality
During major SMP upgrades, customers often face long and repetitive regression testing cycles to ensure existing functionalities remain intact. The Automated Test Framework (ATF) addresses this challenge by automating those tests, significantly reducing the time and effort required for validation.
By using ATF, customers can accelerate upgrade timelines, minimize risks, and maintain consistent quality across deployments — ensuring a faster, smoother, and more reliable upgrade experience.
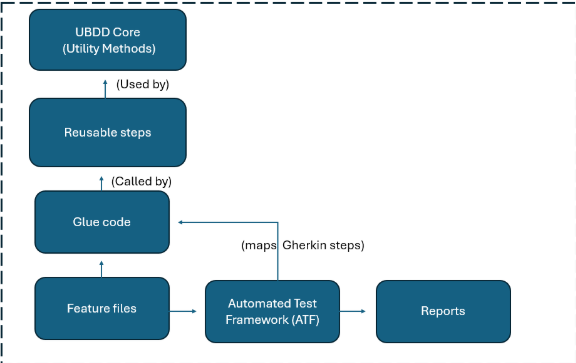
How the Components Fit Together
Here’s a diagram illustrating the core components and their relationships in the ATF ecosystem:
- Feature Files: Business-readable scenarios written in Gherkin.
- Glue Code: Bridges feature steps to reusable test functions.
- Reusable Steps: Wrap around UBDD Core utilities providing ready-to-use test actions.
- UBDD Core: Core utility implementations for common application functions.
- ATF: The conductor managing test execution, coordination, and reporting with Cucumber reports.
ShapeOut-of-the-Box (OOTB) Components
The framework provides a set of predefined step definitions and implementations that cover standard product functionalities. In addition, the framework includes an example feature file, “Startup” workflow, to demonstrate best practices and serve as a reference for structuring scenarios.
Customizable Components
While OOTB steps cover core product behavior, customers are expected to:
- Create feature files for their own workflows
- Define custom step definitions and implementations for behavior that goes beyond standard product functionality
- This approach ensures that customers can tailor automation to their unique business processes while still leveraging the robustness of the existing framework.
Final Thoughts
The SMP Automated Test Framework (ATF) streamlines test automation by combining modular test ownership, reusable building blocks, and powerful orchestration into one unified system. It enables SMP customers to validate their custom-developed workflows and configurations with speed and precision. Instead of manually verifying every step in complex processes after an update or change, ATF automates those tests to ensure workflows continue to perform as intended.
By using ATF, SMP customers can reduce manual testing time, identify issues early, and maintain the integrity of their custom solutions during upgrades. This leads to faster deployments, greater reliability, and increased confidence in the stability of their environment.
In short, ATF ensures that improvements and new features are delivered without compromising reliability or efficiency, helps teams to maintain high quality and performance while driving innovation.

